Token Authentication Specification
Estimated reading time: 7 minutesDocker Registry v2 authentication via central service
This document outlines the v2 Docker registry authentication scheme:
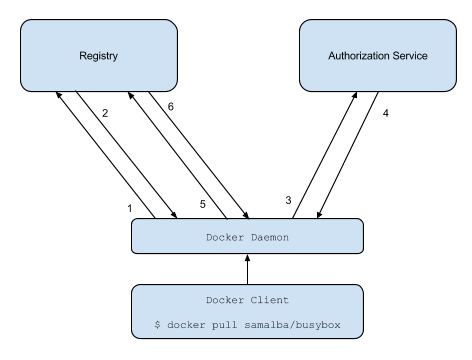
- Attempt to begin a push/pull operation with the registry.
- If the registry requires authorization it will return a
401 UnauthorizedHTTP response with information on how to authenticate. - The registry client makes a request to the authorization service for a Bearer token.
- The authorization service returns an opaque Bearer token representing the client’s authorized access.
- The client retries the original request with the Bearer token embedded in the request’s Authorization header.
- The Registry authorizes the client by validating the Bearer token and the claim set embedded within it and begins the push/pull session as usual.
Requirements
- Registry clients which can understand and respond to token auth challenges returned by the resource server.
- An authorization server capable of managing access controls to their resources hosted by any given service (such as repositories in a Docker Registry).
- A Docker Registry capable of trusting the authorization server to sign tokens which clients can use for authorization and the ability to verify these tokens for single use or for use during a sufficiently short period of time.
Authorization Server Endpoint Descriptions
The described server is meant to serve as a standalone access control manager for resources hosted by other services which wish to authenticate and manage authorizations using a separate access control manager.
A service like this is used by the official Docker Registry to authenticate clients and verify their authorization to Docker image repositories.
As of Docker 1.6, the registry client within the Docker Engine has been updated to handle such an authorization workflow.
How to authenticate
Registry V1 clients first contact the index to initiate a push or pull. Under
the Registry V2 workflow, clients should contact the registry first. If the
registry server requires authentication it will return a 401 Unauthorized
response with a WWW-Authenticate header detailing how to authenticate to this
registry.
For example, say I (username jlhawn) am attempting to push an image to the
repository samalba/my-app. For the registry to authorize this, I will need
push access to the samalba/my-app repository. The registry will first
return this response:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Docker-Distribution-Api-Version: registry/2.0
Www-Authenticate: Bearer realm="https://auth.docker.io/token",service="registry.docker.io",scope="repository:samalba/my-app:pull,push"
Date: Thu, 10 Sep 2015 19:32:31 GMT
Content-Length: 235
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000
{"errors":[{"code":"UNAUTHORIZED","message":"access to the requested resource is not authorized","detail":[{"Type":"repository","Name":"samalba/my-app","Action":"pull"},{"Type":"repository","Name":"samalba/my-app","Action":"push"}]}]}
Note the HTTP Response Header indicating the auth challenge:
Www-Authenticate: Bearer realm="https://auth.docker.io/token",service="registry.docker.io",scope="repository:samalba/my-app:pull,push"
This format is documented in Section 3 of RFC 6750: The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework: Bearer Token Usage
This challenge indicates that the registry requires a token issued by the
specified token server and that the request the client is attempting will
need to include sufficient access entries in its claim set. To respond to this
challenge, the client will need to make a GET request to the URL
https://auth.docker.io/token using the service and scope values from the
WWW-Authenticate header.
Requesting a Token
Defines getting a bearer and refresh token using the token endpoint.
Query Parameters
service- The name of the service which hosts the resource.
offline_token- Whether to return a refresh token along with the bearer token. A refresh token is capable of getting additional bearer tokens for the same subject with different scopes. The refresh token does not have an expiration and should be considered completely opaque to the client.
client_id- String identifying the client. This client_id does not need to be registered with the authorization server but should be set to a meaningful value in order to allow auditing keys created by unregistered clients. Accepted syntax is defined in [RFC6749 Appendix A.1](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6749#appendix-A.1).
scope- The resource in question, formatted as one of the space-delimited entries from the
scopeparameters from theWWW-Authenticateheader shown above. This query parameter should be specified multiple times if there is more than onescopeentry from theWWW-Authenticateheader. The above example would be specified as:scope=repository:samalba/my-app:push. The scope field may be empty to request a refresh token without providing any resource permissions to the returned bearer token.
Token Response Fields
token- An opaque
Bearertoken that clients should supply to subsequent requests in theAuthorizationheader. access_token- For compatibility with OAuth 2.0, we will also accept
tokenunder the nameaccess_token. At least one of these fields must be specified, but both may also appear (for compatibility with older clients). When both are specified, they should be equivalent; if they differ the client's choice is undefined. expires_in- (Optional) The duration in seconds since the token was issued that it will remain valid. When omitted, this defaults to 60 seconds. For compatibility with older clients, a token should never be returned with less than 60 seconds to live.
issued_at- (Optional) The RFC3339-serialized UTC standard time at which a given token was issued. If
issued_atis omitted, the expiration is from when the token exchange completed. refresh_token- (Optional) Token which can be used to get additional access tokens for the same subject with different scopes. This token should be kept secure by the client and only sent to the authorization server which issues bearer tokens. This field will only be set when `offline_token=true` is provided in the request.
Example
For this example, the client makes an HTTP GET request to the following URL:
https://auth.docker.io/token?service=registry.docker.io&scope=repository:samalba/my-app:pull,push
The token server should first attempt to authenticate the client using any
authentication credentials provided with the request. From Docker 1.11 the
Docker engine supports both Basic Authentication and OAuth2 for
getting tokens. Docker 1.10 and before, the registry client in the Docker Engine
only supports Basic Authentication. If an attempt to authenticate to the token
server fails, the token server should return a 401 Unauthorized response
indicating that the provided credentials are invalid.
Whether the token server requires authentication is up to the policy of that access control provider. Some requests may require authentication to determine access (such as pushing or pulling a private repository) while others may not (such as pulling from a public repository).
After authenticating the client (which may simply be an anonymous client if
no attempt was made to authenticate), the token server must next query its
access control list to determine whether the client has the requested scope. In
this example request, if I have authenticated as user jlhawn, the token
server will determine what access I have to the repository samalba/my-app
hosted by the entity registry.docker.io.
Once the token server has determined what access the client has to the
resources requested in the scope parameter, it will take the intersection of
the set of requested actions on each resource and the set of actions that the
client has in fact been granted. If the client only has a subset of the
requested access it must not be considered an error as it is not the
responsibility of the token server to indicate authorization errors as part of
this workflow.
Continuing with the example request, the token server will find that the
client’s set of granted access to the repository is [pull, push] which when
intersected with the requested access [pull, push] yields an equal set. If
the granted access set was found only to be [pull] then the intersected set
would only be [pull]. If the client has no access to the repository then the
intersected set would be empty, [].
It is this intersected set of access which is placed in the returned token.
The server then constructs an implementation-specific token with this intersected set of access, and returns it to the Docker client to use to authenticate to the audience service (within the indicated window of time):
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
{"token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJFUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IlBZWU86VEVXVTpWN0pIOjI2SlY6QVFUWjpMSkMzOlNYVko6WEdIQTozNEYyOjJMQVE6WlJNSzpaN1E2In0.eyJpc3MiOiJhdXRoLmRvY2tlci5jb20iLCJzdWIiOiJqbGhhd24iLCJhdWQiOiJyZWdpc3RyeS5kb2NrZXIuY29tIiwiZXhwIjoxNDE1Mzg3MzE1LCJuYmYiOjE0MTUzODcwMTUsImlhdCI6MTQxNTM4NzAxNSwianRpIjoidFlKQ08xYzZjbnl5N2tBbjBjN3JLUGdiVjFIMWJGd3MiLCJhY2Nlc3MiOlt7InR5cGUiOiJyZXBvc2l0b3J5IiwibmFtZSI6InNhbWFsYmEvbXktYXBwIiwiYWN0aW9ucyI6WyJwdXNoIl19XX0.QhflHPfbd6eVF4lM9bwYpFZIV0PfikbyXuLx959ykRTBpe3CYnzs6YBK8FToVb5R47920PVLrh8zuLzdCr9t3w", "expires_in": 3600,"issued_at": "2009-11-10T23:00:00Z"}
Using the Bearer token
Once the client has a token, it will try the registry request again with the
token placed in the HTTP Authorization header like so:
Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJFUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IkJWM0Q6MkFWWjpVQjVaOktJQVA6SU5QTDo1RU42Ok40SjQ6Nk1XTzpEUktFOkJWUUs6M0ZKTDpQT1RMIn0.eyJpc3MiOiJhdXRoLmRvY2tlci5jb20iLCJzdWIiOiJCQ0NZOk9VNlo6UUVKNTpXTjJDOjJBVkM6WTdZRDpBM0xZOjQ1VVc6NE9HRDpLQUxMOkNOSjU6NUlVTCIsImF1ZCI6InJlZ2lzdHJ5LmRvY2tlci5jb20iLCJleHAiOjE0MTUzODczMTUsIm5iZiI6MTQxNTM4NzAxNSwiaWF0IjoxNDE1Mzg3MDE1LCJqdGkiOiJ0WUpDTzFjNmNueXk3a0FuMGM3cktQZ2JWMUgxYkZ3cyIsInNjb3BlIjoiamxoYXduOnJlcG9zaXRvcnk6c2FtYWxiYS9teS1hcHA6cHVzaCxwdWxsIGpsaGF3bjpuYW1lc3BhY2U6c2FtYWxiYTpwdWxsIn0.Y3zZSwaZPqy4y9oRBVRImZyv3m_S9XDHF1tWwN7mL52C_IiA73SJkWVNsvNqpJIn5h7A2F8biv_S2ppQ1lgkbw
This is also described in Section 2.1 of RFC 6750: The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework: Bearer Token Usage
registry, on-prem, images, tags, repository, distribution, Bearer authentication, advanced